Low Frequency (50/60Hz) Single Phase AC |
|
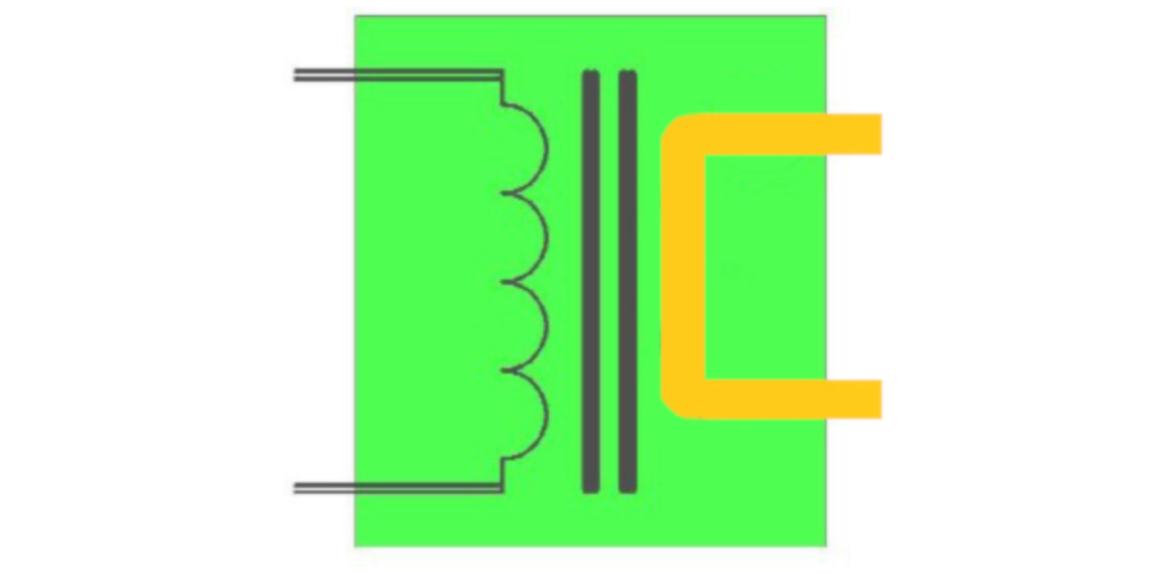
Prior to the year 2000, the low frequency AC welding transformer was by far the most widely used power transfer system. The power frequency on
the primary of the transformer is 50/60 Hz with a nominal primary voltage of 220V, 380V, 480V, or 600V. The power to the
transformer is controlled by inverse parallel SCRs in the welding control. The secondary voltage varies from 3 volts upwards
to 30 volts depending on the turns ratio between the primary and secondary windings. In determining the size of transformer
necessary for a specific welding task, one first determines the required current output for the weld, then determines the voltage
equired to push the current through the resistance of the tools and the work piece. The total impedance (inductive and resistive)
must be accounted for determining the required voltage. |
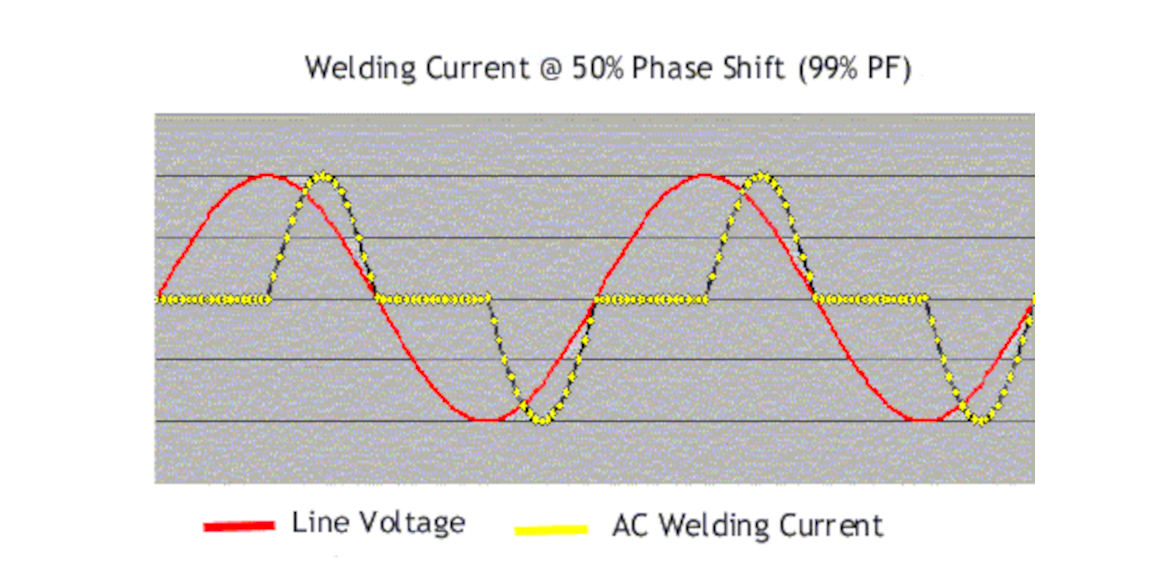
Single Phase AC Current Waveform
The welding current appears as shown to the right for single phase AC welders. The graph shows two cycles of the time period. Notice that in between pulses of
alternating polarity, there is time when current is zero. This is sometimes referred as "inter-cycle cooling" period.
You can see a comparison of a Low Frequency AC weld current pattern and an MFDC weld current pattern in page 7 in the description of the
Mid Frequency (400 - 2000Hz) to DC weld transformer.
|
|
|
To Top